Choosing the Right Flow Meter: Types & Applications
Flow meters measure the flow rate of fluids in a wide range of industries. These instruments are crucial in measuring the flow of liquids, gases, and slurries, making them essential. Optimal performance and accurate measurements require selecting the correct flow meter. Doing so is critical for various applications.
Types of Flow Meters and Their Applications
1. Differential Pressure Flow Meters
Fluid flow is measured using differential pressure flow meters, making them a popular device in today's world. The meter calculates pressure loss via a pipe restriction, leading to fluid flow calculation. The fundamental principle of operation indicates that the pressure drop on the meter is proportional to the rate of flow squared. The primary element causes kinetic energy change, inducing a differential pressure, and the secondary element gauges the pressure differential. With over 50% of all liquid flow measurement applications using this type, it is suitable for various industries.
Types of Differential Pressure Flow Meters
- Orifice Plates: These are cost-effective and simple, they use a flat plate with a hole to make a pressure drop.
- Variable Area Meters (Rotameters): These devices use a float inside a tapered tube to visibly display the flow rate.
- Venturi Tubes: Venturi tubes provide reduced pressure drops and are perfect for high-flow applications because of their tapered design.
- Pitot Tubes: These tubes, which are typically utilized for single-point measurements, depend on the fluid's velocity pressure.
2. Velocity Flow Meters
Velocity flow meters are instruments that measure the speed of a fluid to calculate its flow rate. They are mostly used in situations where the fluid is moving at a relatively constant speed. There are several types of velocity flow meters, and each type takes a different approach to measuring velocity.
Types of Differential Pressure Flow Meters
- Turbine Meters: These meters have a rotor with blades that spin in tandem with the flow to produce pulses that are proportionate to the velocity of the fluid
- Ultrasonic Flow Meters: Ultrasonic signals pass through fluid and their velocity is measured for accurate flow rate determination.
- Vortex Meters: These devices provide precise readings by using pressure sensors to identify the vortices formed as the fluid passes over an impediment.
3. Positive Displacement Flow Meters
For positive displacement flow meters to function, the fluid must first be divided into precisely measured increments before being moved forward. These meters are appropriate for uses requiring accurate volume readings.
Types of Positive Displacement Flow Meters
- Reciprocating Piston Meters: This instrument measures fluid volume by moving a piston back and forth.
- Gear Meters: These meters are appropriate for high-viscosity fluids because of their interlocking rotating gears that regulate fluid flow.
- Oval Gear Meters: They produce accurate readings by using oval-shaped gears.
- Lobe Meters: These displace fluid axially between two rotors, ensuring accurate measurements.
- Rotary Piston Meters: These meters use a rotating piston to gauge the amount of fluid displaced.
4. Mass Flow Meters
Mass flow meters directly measure mass flow rate, providing accurate measurements despite changes in fluid properties. They are commonly used where mass is an essential parameter.
Types of Mass Flow Meters
- Coriolis Flow Meters: Suitable for a range of gas and liquid applications, these meters measure mass flow precisely by utilizing the Coriolis effect.
- Thermal Mass Flow Meters: They work by transferring heat from a heated sensor to the fluid in flow, with mass flow being proportionate to heat loss.
5. Open Channel Flow Meters
The purpose of open channel flow meters is to measure the flow via open channels, like canals, rivers, and wastewater treatment plants. They measure the depth and velocity of the liquid as it flows to calculate flow rates.
Types of Open Channel Flow Meters
- Weirs: Weirs are structures placed in the flow path to create a measurable flow level, allowing for flow rate calculations.
- Flumes: Flumes are specialized channels that constrict and expand the flow, facilitating accurate flow rate measurements.
- Acoustic Doppler Velocimeters (ADVs): ADVs measure the Doppler shift of the reflected signals using acoustic waves to estimate flow velocity.
How to Choose the Right Flow Meter
A number of important considerations should be made when selecting the appropriate flow meter for your application:
- Flow Measurement Type: Determine whether momentum (velocity), volumetric, or mass flow measurement is more suitable for your needs.
- Media Type and Conditions: Consider the type of media (liquid, gas, or slurry) and any specific conditions, such as the presence of particulates and viscosity.
- Flow Range: Define the required flow range, including minimum and maximum readings.
- Required Accuracy: Assess the level of accuracy required for your measurements.
- Environmental Considerations: Account for any special installation considerations, such as hygienic installations, ATEX zone requirements, or the need for tamper-proof readings.
Choosing the appropriate flow meter is crucial for accurate and reliable flow rate measurements in various industries. To select the best option that caters to your specific requirements, it is important to have a good understanding of the general applications and working principles of different types of flow meters such as differential pressure, velocity, positive displacement, mass, and open channel flow meters. Our guide outlines the key factors you need to consider when choosing a flow meter, such as the specifications of your application and the accuracy of measurements required for your industry. By taking these elements into account, you can ensure that you choose the right flow meter that provides precise measurements for your sector.
Torque Wrench Calibration: A Guide for Maintaining Accuracy and Compliance
In so many industries, ensuring torque wrench calibration is crucial - manufacturing, aviation, automotive, nuclear, and wind energy are just a few that come to mind. With poorly calibrated torque wrenches, the potential for joint connection failure skyrockets, making these precision instruments essential for fastening processes. Testing these wrenches for accuracy and reliability isn't just a nice-to-have - it's an absolute necessity. There are many different types of torque wrenches, each capable of measuring a wide range of torque values. Routine calibration and the right tools are absolutely necessary for ensuring accurate torque measurements that stand up to even the toughest conditions.
Why Calibrate a Torque Wrench
There are many factors that affect the accuracy of your torque wrench and how it functions. Just like any other device, wear and tear can cause it to gradually lose its accuracy over time. The environment in which it is used also plays a role, including the temperature and humidity conditions. Overload is another factor, and it is recommended to recalibrate the torque wrench when it is subjected to an overload equal to or more than 25% of the maximum. Failing to have your torque wrench calibrated could cause safety hazards, increased costs, a decline in output quality, and failure to comply with regulations.
How Often Should You Calibrate a Torque Wrench
In general, the standard practice for calibrating a torque wrench is every 5,000 cycles or every 12 months, whichever comes first. However, for more assurance, it is recommended to schedule calibration every 6 months. Despite the recommended schedule, it is still important to consider other factors like wear and tear, frequency of use, and working environment.
Types of Torque Wrenches and Calibration
Different designs and mechanisms characterize various torque wrench types, like beam and electronic wrenches. As a result, the calibration procedures must be tailored to meet their particular features, contributing to their distinctiveness.
Some of the most commonly used torque tools include torque wrenches, torque screwdrivers, torque multipliers, and torque testers. These tools play a key role in tightening nuts and bolts to exact torque levels, but their dependability and precision hinge on accurate calibration.
Calibration Method and Process for Torque Wrenches
The core of torque wrench calibration lies in the use of a torque calibration tester, a device that applies a known force to the torque wrench. The applied force is measured by this tester, which also highlights any discrepancies between the applied force and the torque wrench readings. The torque wrench is then adjusted such that its readings match the force that the tester is applying. A calibration certificate, indicating adherence to industry standards, is ultimately issued after this rigorous process is completed numerous times to ensure accuracy. For consistency and precision, it is crucial to adhere to the ISO 6789 standard, which acts as a thorough manual for the precise steps required in torque wrench calibration.
Depending on the torque wrench being used, different calibration techniques may be used. Calibration for beam-type torque wrenches requires inspecting the pointer while the tool is at rest and, if required, making modifications to the pointer shaft. On the other hand, electronic torque wrenches follow the international standard protocol to guarantee precise calibration. No matter what kind of torque wrench is used, it's important to understand that accurate training is required to carry out calibration efficiently and precisely.
Choosing the Right Calibration Service Provider
If you have already identified the need for torque wrench calibration, it is a top priority to choose a provider that is suitable for your business or project. One notable solution provider in the calibration industry is Micro Precision, with over 50 years of experience in torque wrench calibration and a team of experienced technicians and metrologists.
The right service provider will offer more than just basic calibration. It's important that they assess your specific equipment's unique requirements. Take the following factors into consideration when choosing a torque wrench calibration service provider:
- Accreditation
- Expertise and Experience
- Calibration Equipment
- Turnaround Time
- Future Trends in Torque Wrench Calibration
The Future of Torque Wrench Calibration
The calibration of torque wrenches is changing as technology progresses. Industry leaders like Micro Precision are at the forefront of innovation in this constantly shifting environment. In order to enhance calibration procedures and accuracy, they are always investigating new technologies and strategies.
The use of smart technology, such as smart torque calibration systems, is one of the prominent trends in torque wrench calibration. These advancements frequently come with attributes like real-time monitoring, data analytics, and remote calibration. This not only improves accuracy but also offers insightful data for quality assurance and preventative maintenance.
A crucial tool for ensuring secure joint connections, the torque wrench is a hand-held item that requires regular calibration. With its ability to prevent failures and maintain precision, this instrument is used across various industries to uphold the integrity of crucial applications. Calibration is therefore mandatory to fortify the tool's accuracy and reliability and ensure consistent optimal performance. By adhering to fundamental calibration practices and implementing them regularly, industries can continue to make use of the torque wrench with confidence.
Onsite Calibration: Overcoming Calibration Challenges
Delays and inconveniences can be some of the nightmares that managers and businesses often encounter. Whenever possible, efforts are made to streamline processes, making them more efficient and convenient.
On-site equipment calibration is one of the most efficient solutions that industries use to improve their processes and avoid problems, providing a range of advantages and addressing many concerns and challenges faced by businesses and projects.
Advantages of Onsite Calibration
Addressing Environmental Variability
Environmental factors play a big role in the performance of instruments. Elements such as temperature, humidity, and air pressure can affect the results of measurements. For instance, a study on the automatic and manual calibration of an office building energy model showed that the effectiveness of the calibration methods can differ depending on the environmental conditions. Therefore, on-site calibration provides peace of mind, as the equipment is calibrated in its actual operating environment.
Minimizing Downtime and Lost Productivity
Downtime can have a significant impact on many aspects of a business, including lost productivity, delays, and decreased revenue. Calibration is essential for maintaining the accuracy of equipment and avoiding downtime. On-site calibration can be especially beneficial, as it allows the calibration process to be performed in the actual facility, eliminating the need for shipping and transportation, which can save time and money.
Customized Calibration for Specialized Equipment
One of the great advantages of onsite calibration, compared with offsite calibration, is its flexibility in providing tailored calibration solutions for specialized equipment. The approach depends on the specific needs of the equipment rather than adopting a one-size-fits-all approach. Calibration techniques, such as adjusting calibration methods, introducing compensatory factors, or even developing novel techniques, may be customized to ensure that highly specialized equipment maintains the accuracy required for its intended purpose. Onsite calibration makes it more efficient to achieve this goal.
Ensuring Compliance and Quality
Many industries require compliance with regulatory standards. The process of shipping equipment back and forth can consume a significant amount of time before it becomes certified. On-site calibration of instruments is an effective way to maintain compliance while minimizing disruptions in operations. It helps ensure that calibration is completed on time, and the equipment meets the regulatory requirements for quality.
Cost-efficiency
On-site calibration offers several cumulative benefits that impact the financial side, including reduced downtime, lower transportation costs, and a lower risk of equipment damage.
For example, if you opt for off-site calibration, you may need to partially or fully pause operations, which can create a gap in production and lead to income loss. Additionally, shipping equipment can be expensive and requires measures to protect the device from damage. There is also a risk of damage during shipping, which may require you to purchase new equipment or have it repaired.
How Onsite Calibration Ensures Data Accuracy
Environmental conditions, like temperature, pressure, and humidity, are simulated during onsite calibration to increase precision in data accuracy. In doing so, equipment calibration is done at the site where it is intended to be used. Real-time feedback adequately recognizes and rectifies deviations to produce dependable measurements. This approach guarantees exactness by ensuring that the equipment duplicates the specific environmental conditions present during typical operations. Better calibration control is achieved with onsite calibration, allowing businesses to adjust frequency and type to meet specific needs while reducing equipment downtime. This individuality and speed come from bypassing the requirement to send equipment externally for calibration, ensuring a seamless and rapid production process.
In conclusion, organizations have a proactive and adaptable option with onsite equipment calibration to improve operations and guarantee data accuracy. In addition to addressing environmental variability, it reduces downtime and costs, offers specialized equipment-specific calibration, assures compliance and quality, and encourages cost efficiency. On-site calibration offers superior control over the calibration process by replicating environmental conditions and providing real-time feedback. This strategy simplifies processes, making it a crucial instrument for corporate excellence and efficiency.
In search of a trusted onsite calibration service provider? Get a free quote now.
Rent Calibrated Equipment: The Smart Way to Get the Job Done
To acquire precise measurements there’s a need for a reliable tool instrument. However, measuring equipment can be quite expensive when purchasing a new one. It may not be feasible for every project or business. This is where equipment rentals come in very handy, it is a great alternative to purchasing. You even get your money’s worth if you rent an instrument that has already been calibrated up to standards.
The Benefits of Renting a Calibrated Instrument
Renting calibrated equipment has a number of benefits over buying one. Cost savings are the most evident perk. You can save money by renting rather than buying a new instrument, which has a hefty upfront cost. This is particularly advantageous for companies or projects that only need it for a short period of time.
Access to cutting-edge technology is another benefit. You can select from a variety of instruments, including the latest and most advanced versions, when you hire a calibrated instrument. By doing this, you can employ the most precise and effective equipment without having to shell out a large amount.
Additionally, renting a calibrated instrument removes the need for maintenance and calibration. These could consume more time and it is costly when you rent from companies like Micro Precision, their technicians make sure that the instruments are ready for use and can deliver accurate measurements through tedious calibration.
How to Rent a Calibrated Instrument
Renting a calibrated instrument is a simple process.
- Determine your specific needs: Identify the type of measurements needed to be taken and the level of precision required.
- Research a trusted rental company. Look into the credentials and experiences that the company has. An accredited calibration company, such as Micro Precision, is highly recommended since its services go beyond just instrument rental.
- Once you’ve chosen the right company, contact them to discuss what you’re looking for. It is also a good idea to ask about the process, the condition of the equipment, and the rental period.
Tips for Renting a Calibrated Instrument
To have a worry-free rental process, here are some tips to consider:
- Reserve the equipment in advance to ensure availability.
- Know and read through all the rental agreements. Inquire about additional fees and insurance requirements.
- Before renting, inspect the equipment for any damages.
- Request for a demonstration on how to use the equipment.
- Return the instrument on or before the agreed date to avoid any late fees.
Renting a calibrated instrument is a cost-effective and convenient option for businesses and projects that require precision measurements. By following these tips and choosing a reputable rental company, you can ensure accurate results without breaking the bank. So the next time you need a precision instrument, consider renting instead of purchasing.
Looking for an experienced equipment rental company? Look no further, Micro Precision has a variety of instruments available for rental. Contact us to learn more.
Seeking an experienced equipment rental provider? Your search ends here – Micro Precision offers a wide range of rental instruments. Reach out to us for further details.
Why NIST Traceable Calibration Matters: Ensuring Accurate Measurements
Countless industries rely heavily on accurate measurements. Precision is not just a "nice-to-have" factor, but often is a requirement, especially if we're talking about product quality and ensuring safety. In the world of calibration, a standard is required, leading us to the topic of NIST traceable calibration.
What is Traceable Calibration?
Traceable calibration refers to a highly reliable calibration technique that can be traced back to a national standard. In other words, it allows for a trustworthy reference point to be used to correlate the measurements taken during the calibration process. This ensures that the calibration results are highly accurate and can be trusted with confidence.
What is NIST Traceable Calibration?
Calibration following NIST standards requires the utilization of calibrated standards derived from NIST, the National Measurement Institute of the United States. NIST holds responsibility for the maintenance of the nation's measurement standards.
NIST traceable calibration is a highly valued and superior form of calibration that's mandatory for numerous industries and uses. Its necessity is particularly important in areas where precision is a vital factor for safety or quality assurance purposes.
Industries Requiring NIST Traceable Calibration
NIST traceable calibration is a dependable and rigorous standard that numerous industries rely on. Take a look at some examples below:
- Aerospace: Whether we're talking about navigation systems or aircraft engines, the high stakes mean that perfection is the key.
- Research & Development: Accuracy is crucial in R&D. To get accurate results, instruments utilized in laboratories doing cutting-edge research must be calibrated.
- Manufacturing: Precision is a great factor in quality control in this industry. It is applicable in gauges, machinery, and other tools that involve the quality of the manufactured products.
- Pharmaceuticals: Pharmaceutical labs and their instruments rely on precise measurements for safe and effective medication production.
- Healthcare: NIST traceable calibration is crucial in medical facilities where precise measurements can be the difference between life and death. Diagnostic equipment and blood pressure monitors demand this calibration for the safety of patients.
Types of NIST Traceable Calibration
NIST traceable calibration can be performed on a wide variety of equipment that encompasses various types:
- Electrical Calibration: This covers equipment that ensures electrical measurements such as multimeters and oscilloscopes.
- Mechanical Calibration: Some of these instruments are torque wrenches, pressure gauges, and balances.
- Thermal Calibration: Instruments that are used to measure temperature, such as infrared thermometers and thermocouples, and any equipment that is subject to thermal calibration.
- Optical Calibration: Optical devices like spectrophotometers and microscopes must undergo optical calibration to provide accurate results.
Benefits of NIST Traceable Calibration
NIST traceable calibration provides numerous benefits across various industries. First off, it vastly improves measurement precision and consistency, guaranteeing that tools and equipment deliver accurate and reliable findings. Reduced margins for mistakes result from this increased accuracy, which is vital in industries where precision is key.
Additionally, NIST traceable calibration is essential for guaranteeing adherence to strict regulatory criteria. Many industries have tight restrictions, and using calibration techniques traceable to NIST helps businesses comply with these rules quickly and prevents penalties or other legal issues.
This calibrating technique also enhances the overall quality of the goods and services. Companies may provide higher-quality goods and services, boosting client happiness and trust, by keeping consistently accurate measurements. NIST traceable calibration ultimately encourages increased customer confidence in the dependability and accuracy of the goods and services they get.
Not only a technical procedure, NIST traceable calibration is a cornerstone of accuracy and dependability in a variety of businesses. It guarantees that the measures used to inform important decisions are precise, reliable, and up to the highest standards. The advantages of NIST traceable calibration are crucial for guaranteeing the quality and safety of your goods and services, regardless of whether you work in the aerospace, healthcare, manufacturing, or research sectors.
Looking for a reliable calibration service provider that ensures NIST traceability? Micro Precision can help! Contact us for a quote or to get started.
Determining the Optimal Gage Block Calibration Frequency
Regularly performing gage block calibration is crucial in the manufacturing and engineering sectors as it ensures consistent, reliable, and precise measurements, maintaining the quality of goods and procedures. One crucial aspect of this process is determining the frequency of calibration. This article aims to provide more information on the factors that influence the best frequency for calibrating gage blocks.
What is Gage Block Calibration?
>Gage block calibration is the process of comparing a gage block's readings to those of a reference standard. Comparing a gage block's readings to a reference standard is known as gage block calibration. To make sure that the gage block is producing reliable readings, this procedure is required. The usage frequency, environmental conditions, and the particular requirements of the sector or application are just a few of the variables that can affect how frequently gage blocks need to be calibrated.
Importance of Calibration Standards
Calibration standards are highly important in the gage calibration process. They serve as a benchmark against which the measurements of the gage block can be compared. These are typically established by international bodies such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
Compliance with these calibration standards ensures that measurements are consistent and dependable, regardless of where or when they are taken. This constancy is essential in fields like aerospace, automotive, and medical device manufacture, where accuracy is of the utmost importance.
Determining the Optimal Gage Block Calibration Frequency
Determining the optimal gage block calibration frequency is not a one-size-fits-all process. It requires a careful consideration of several factors:
- Frequency of Use: Calibration may need to be done more often for gage blocks that are frequently more utilized. This is due to the potential for wear and tear, which has an impact on the precision of measurements.
- Enviromental Conditions: The conditions in which the gage blocks are being used play a big role in determining calibration frequency. Drastic temperature changes or high levels of humidity.
- Industry Requirements: Each industry may have set different requirements for gage block calibration frequency.
- Historical Performance: The frequency of calibration can also be determined based on the historical performance of the equipment. Keeping track of how long the gage block has been able to maintain its accuracy is also a great indicator.
The Role of Gage Calibration in Quality Assurance
Maintaining the quality of products and processes is crucial with gage calibration. It ensures accuracy and consistency in measurements. Interestingly, gage block calibration has the added benefit of early detection of any issues relating to gage blocks. This can save a lot of time if timely repairs or replacements are made.
The accuracy and reliability of measurements are key factors that determine the quality of products and processes. To achieve this, calibration frequency for gage blocks must be carefully evaluated based on various considerations. Strictly abiding by calibration standards and consistently conducting calibrations will guarantee the accuracy and reliability of measurements, which is essential for businesses to maintain the quality of their operations.
Get a reliable calibration service provider for gage blocks. Contact us to learn more and get a free quote.
Calibration Certificates: Its Importance in Ensuring Accurate Measurements
In maintaining quality control and compliance in different sectors, calibration certificates are incredibly important. These certificates offer documented proof that a measuring instrument has been calibrated against a traceable standard, certifying its accuracy and reliability. The role they play in ensuring precise measurements in various industries cannot be overemphasized. This blog post delves into the significance of calibration certificates and their contribution to various sectors.
Why Calibration Certificates Matter
Ensuring Measurement Accuracy
Calibration certificates offer assurance when it comes to accurate and reliable instrument measurements. They minimize measurement errors by verifying that the equipment has been calibrated against traceable standards.
Compliance with Standards and Regulations
The certificate signifies compliance with the industry standards and regulations. Compliance with the standards is crucial for many industries, especially in healthcare, aerospace, and manufacturing. It is considered evidence that the equipment used is accurate and precise.
Quality Control and Process Improvement
Quality control procedures require calibration certificates. They aid in locating and eliminating any errors or variations in measuring devices. Process optimization and improvement are aided by routine calibration and certification.
 Types of Calibration Certificates
Types of Calibration Certificates
In order to guarantee the accuracy and reliability of measurement instruments, there are three main forms of calibration certificates.
Traceable Calibration Certificates
Across several industries, Traceable Calibration Certificates have earned immense respect by creating a vital connection between a national or international standard and the instrument being calibrated. This connection is instrumental in establishing a comprehensive and documented chain of measurement traceability, making these certificates invaluable.
Accredited Calibration Certificates
Accredited Calibration Certificates are issued by accredited calibration laboratories. These certificates give an extra level of assurance to the calibration procedure. They are frequently required for sectors that must adhere to strict regulatory standards in order to ensure compliance and dependability in crucial measures.
In-House Calibration Certificates
Organizations that possess their own calibration facilities can obtain In-House Calibration Certificates. These certificates are suitable for companies that have the necessary skills and resources to conduct calibrations internally. However, it’s important to note that although these certificates hold value within the company, they may not always be recognized and accepted outside of it. The type of calibration certificate that a company chooses depends on its specific needs, regulatory obligations, and the level of industry recognition and trust required.
Importance of Regular Calibration
Ensuring Long-Term Accuracy
Regular calibration is an important factor in maintaining an equipment’s accuracy over time. Wear and tear naturally occur and can cause a decline in performance. To avoid this and further issues, a regular calibration schedule is highly recommended.
Meeting Regulatory Requirements
Many industries place requirements and standards to guarantee safety and avoid legal issues. Compliance with this is necessary to avoid penalties and reputational damage. It is also a way for organizations to show that they are placing high value on quality and compliance.
Cost Savings and Efficiency
Regular calibration helps detect issues earlier. Errors, damages and inaccuracies will eventually cause monetary losses. Examples of these are product recalls, reworks, and process delays.
For precise measurements, ongoing quality control, and regulatory compliance, calibration certificates are essential. They offer formally documented proof of accuracy and dependability, whether they are traceable, accredited, or internal calibration certificates. To guarantee long-term accuracy, satisfy legal requirements, save money, and improve process effectiveness, regular calibration is necessary. Organizations can ensure accurate measurements and keep their competitive edge in the market by giving calibration and certification top priority.
10 Test Equipment that will Elevate your Winemaking Process

Making wine is an art form that requires precision to achieve the perfect taste that winemakers are aiming for. It is a meticulous process that requires the monitoring and analysis of many factors before attaining the right balance, aroma, and texture that make wines exceptional. This cannot be accomplished without the assistance of the appropriate test equipment.
The test equipment you need for a winery will depend on the size and complexity of your operation and the type of wine you are making. However, some of the most common test equipment used in wineries include:
1. pH Meters
Acidity is highly important in winemaking, pH meters help winemakers navigate the fermentation and aging processes by acting as compasses. By ensuring unmatched accuracy in acidity measurements, these cutting-edge tools enable the creation of ideal pH ranges that orchestrate a symphony of flavors. The pH scale, with a range of 0 to 14, determines whether something is acidic or alkaline. While white wines aim for pH 3.0 to 3.5, red wines aim for pH 3.5 to 4.0.
2. Refractometers
Measuring grape ripeness is crucial. Refractometers measure grape sugar content (Brix). This info helps winemakers time harvest and achieve the perfect balance of sweetness and acidity that characterizes wines. Brix influences wine sweetness and grape ripeness from vineyard to cellar.
3. Spectrophotometers
Color and stability, two crucial components of wine’s visual appeal, are precisely evaluated by a spectrophotometer. It operates by shining light through wine and measuring the amount of different wavelengths that are absorbed. This reveals the color of the wine as well as the concentrations of various compounds, such as tannins. By monitoring oxidation rates, spectrophotometers can also evaluate stability while protecting wine from the flavor and color deterioration brought on by this chemical process.
4. Gas Chromatographs
Winemakers can evaluate the quality and track the aging of wines by identifying and measuring volatile compounds in wine using a gas chromatograph. Wine’s personality is shaped by the complex interplay of volatile compounds, which coordinates flavors and aromas. Winemakers can fine-tune their production methods with the help of gas chromatographs, which reveal hidden secrets and allow them to create wines with greater complexity and depth.
5. Osmometer
Osmotic pressure is an invisible force that affects composition in addition to the visible elements of wine. Osmometers, these silent watchmen, measure solute concentrations and give winemakers a better understanding of the fluid environments they travel through. Winemakers can use osmotic pressure’s potential to create wines with precise character and identity by understanding its effects.
6. Density Meters
The harmony of a well-crafted wine depends not only on its taste, but also on its density. Density Meters These mathematicians deciphered the complex relationship between density and alcohol content. With their help, winemakers perfect the symphony of alcohol, resulting in the perfect crescendo that bears witness to authenticity.
7. Sulfur Dioxide (SO2) Analyzers
Color and stability are essential elements of wine’s visual appeal. A spectrophotometer is a tool that can be used to measure these properties with precision. Sulfur dioxide (SO2) plays a crucial role in wine preservation beyond flavor. SO2 analyzers monitor and regulate SO2 levels to protect wine from undesirable influences, giving it time to mature.
8. Titrator
Another way to measure the acidity of wine is by using a titrator. A wine sample is titrated by adding a known quantity of base until the pH reaches a predetermined value. The wine’s acidity is determined by the amount of base that has been added. With a titrator, winemakers can adjust and monitor the acidity during the fermentation stage.
9. Spectrometer
Spectrometers are used by winemakers to analyze the chemical makeup of their wines and monitor the aging process. Spectrometers are instruments that measure the absorption of light at various wavelengths and can be used to identify the various chemicals in wine. The flavor, color, and level of alcohol in the wine can all be determined using this information. Winemakers can enhance their wines by using spectrometers to monitor changes in the chemical composition of the wine over time.
10. Hydrometer
The hydrometer’s remarkable features enable it to measure liquid density and aid in determining sugar content, alcohol concentrations, and fermentation status. It also helps with calculating alcohol content to ensure that the desired balance and characteristics of the wine are achieved.
Excellent Wine Craftsmanship Through Technology
Wine production is a complex and delicate process that requires the use of sophisticated testing equipment. The right testing equipment can help winemakers achieve the perfect taste, aroma and texture that their customers demand.
The testing equipment most commonly used in breweries includes pH meters, refractometers, spectrophotometers, gas chromatographs, osmometers, density meters, sulfur dioxide (SO2) analyzers, titrators, and spectrometers.
These instruments can measure various factors, including acidity, sugar content, alcohol content, color, and stability. By carefully monitoring these factors, winemakers can ensure their wines are of the highest quality.
Contact Micro Precision if you need used or rental equipment. You may also request a quote if you need calibration services for your winery equipment.
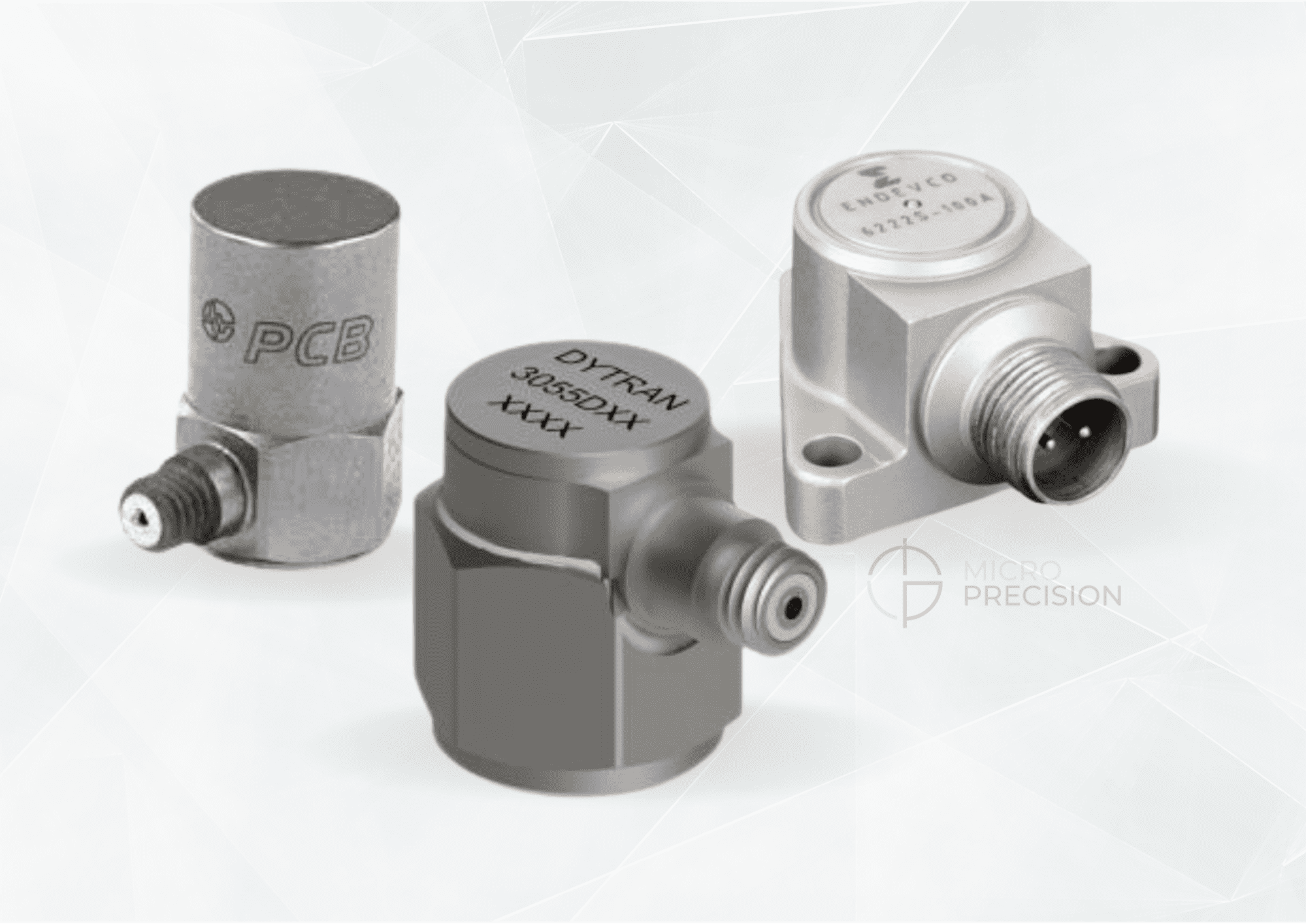
How Accelerometers Work and What They're Used For
Thriving in various environments, modern technology never fails to captivate us with its complexities. Among those contributing to its growth are accelerometers - an innovative invention that have revolutionized the industry with their versatile applications. By detecting acceleration, tilt, and motion, these sensors are used for a vast array of purposes, ranging from smartphones to aircrafts. With the intention of providing insight into the mechanics behind these ingenious devices, this article will explore their numerous applications and the significance of precise calibration.
What is an Accelerometer?
Accelerometers are built to gauge acceleration, i.e., the pace at which an object's speed or direction varies. Such sensors usually have a spring-fixed weight that undulates counter to the acceleration in question. In other words, an accelerometer senses how fast the direction or swiftness of an object transforms.
The degree of acceleration is unveiled by the output, which is processed and amplified by a circuit, after the sensor detects movement and transforms it into an electrical signal.
What Does an Accelerometer Measure?
Accelerometers perform a variety of measurements pertaining to physical quantities. This includes:
- Linear acceleration: The measurement for acceleration in a straight line is expressed in meters per second squared. (m/s²).
- Angular acceleration: The measure of an object's acceleration while rotating around an axis is expressed in radians per second squared. (rad/s²).
- Gravitational force: The measurement of the force of gravity on an object is expressed in newtons. (N).
Different Types of Accelerometers
There are different types of accelerometers that use unique technologies to measure acceleration. The three main types are:
- Capacitive accelerometers: By utilizing the change in capacitance between two plates, these accelerometers are able to produce an electrical signal when subjected to acceleration. It's worth noting that capacitance refers to the ability of two conductors to store an electrical charge.
- Piezoelectric accelerometers: These accelerometers utilize the piezoelectric effect to produce an electrical signal in response to acceleration. The piezoelectric effect is a property of specific materials that enables them to generate an electric charge under mechanical stress.
- MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) accelerometers: The use of miniaturized sensors and electronics has enabled the creation of accelerometers that are highly compact. MEMS accelerometers, specifically, are exceptionally small and lightweight, rendering them perfect for wearable devices and other space-constrained applications.
Applications of Accelerometers
The versatile and useful nature of accelerometers is evident in the wide range of industries that make use of them. In the automotive industry, these devices are integral components of airbag deployment systems, accurately triggering airbags during significant deceleration caused by collisions. Consumer electronics benefit from accelerometers as well, enabling features like screen rotation and gesture recognition on smartphones. Reliable and accurate navigation, flight control, and pilot training are ensured in the aerospace industry thanks to accelerometers. In industrial settings, these devices monitor machinery, analyze vibrations, and optimize manufacturing processes. Sports and healthcare wearables also rely on accelerometers to track physical activity, aid recovery and prevent injuries.
How Often Should I Calibrate My Accelerometer?
Having professionals regularly calibrate accelerometers is crucial to ensure accurate measurements. The calibration frequency will vary depending on the specific application and environment in which the accelerometer is used.
To guarantee precision, some high-stakes applications, such as airbag deployment systems, may call for frequent calibrations, despite the yearly recommendation for accelerometer calibration.
In spite of this, an accelerometer's necessary calibration frequency can be influenced by its operational surroundings. If used in demanding scenarios where vibrations or elevated temperatures exist, more frequent calibration may be mandatory than it would in a less taxing environment.
What Happens If I Don't Calibrate My Accelerometers?
Regular accelerometer calibration is vital for ensuring precise measurements. Incorrect data interpretation due to failure to calibrate can be quite risky, particularly in hazardous situations. A collision could lead to an airbag system malfunction, putting lives in jeopardy due to poor calibration. Don't play a risky game with inaccurate readings and always make sure to calibrate your accelerometers regularly.
Accelerometers are crucial sensors for various applications where accuracy plays a key role. Calibration knowledge and understanding of their functionality will ensure their reliability when in use. If you're enthusiastic about discovering our calibration services for accelerometers, just ask for a free quote catering to your specific model.
Elevating Standards: How ISO 17025 Accreditation Impacts Calibration Services
Equipment and instruments must be calibrated to ensure proper operation, and the ISO 17025 accreditation is critical to elevating standards in the calibration business.
What is ISO/IEC 17025?
ISO/IEC 17025 is a quality management system that sets out the standards for testing and calibration facilities. It is a standard made by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). This serves as a guideline for managing operations and delivering reliable results. The accreditation procedure evaluates a lab's capacity to produce precise and traceable results, the skills of its personnel, the facilities' adequacy, and the effectiveness of its quality management system. Regular audits by an independent third party are required as part of the accreditation process to evaluate the laboratory's adherence to the ISO 17025 standard.
The Benefits of ISO 17025 Accreditation
Becoming an ISO 17025 accredited calibration laboratory presents a wide range of advantages to the business and its partners. Customers are confident that a laboratory is competent in producing accurate findings thanks to ISO 17025 accreditation. Building trust between calibration service providers and their clients requires this assurance. A trustworthy calibration lab that delivers precise and dependable results helps firms save time and money by avoiding manufacturing waste and boosting product quality.
ISO 17025 Accreditation Process
Accreditation according to ISO 17025 is a multi-step process. Prior to becoming accredited, calibration labs must first establish a quality management system that complies with the standard set. All laboratory operations, including test and calibration methods, equipment maintenance, document management, and staff training are covered by this system.
The laboratory must be ready for the initial audit conducted by an independent third party once the quality management stem is in place. The audit evaluates the laboratory's technical proficiency, quality management system, and facilities for conformity with the ISO 17025 standard. The laboratory receives ISO 17025 certification if it complies with the standards of the standard.
Maintaining the ISO/IEC 17025 Accreditation
In order to guarantee that the calibration lab continues to deliver reliable results, maintaining the accreditation is crucial. Regular audits are done and often conducted every two years, this is to guarantee continued adherence to the standard. To ensure passing the audit, conduct internal audits, maintain a document control system, train and improve staff skills, calibrate equipment, proactively check for issues, participate in proficiency testing programs, and conduct regular management reviews.
Audits are used to find non-conformities or instances in which the laboratory is not adhering to the standards. The laboratory is required to take steps to correct or address issues if non-conformities are found. The ISO 17025 certification of the laboratory may be suspended or revoked for failure to rectify non-conformities.
ISO 17025 certification is a crucial part of the calibration industry. Accredited ISO 17025 calibration laboratories have shown their capacity to produce precise and trustworthy results, and they have set a quality management system that complies with global norms. Businesses that depend on calibration services now have the assurance of this accreditation, which helps them decrease equipment downtime, cut down production waste and improve product quality.
It's crucial to select an ISO 17025 accredited calibration lab if you're seeking calibration services. Labs such as Micro Precision, have proven their skill and capacity to provide accurate and dependable findings, assisting companies in achieving their quality and productivity objectives. If you’re looking for a trusted and certified calibration service company to work with, contact us or request a quote.







 Types of Calibration Certificates
Types of Calibration Certificates